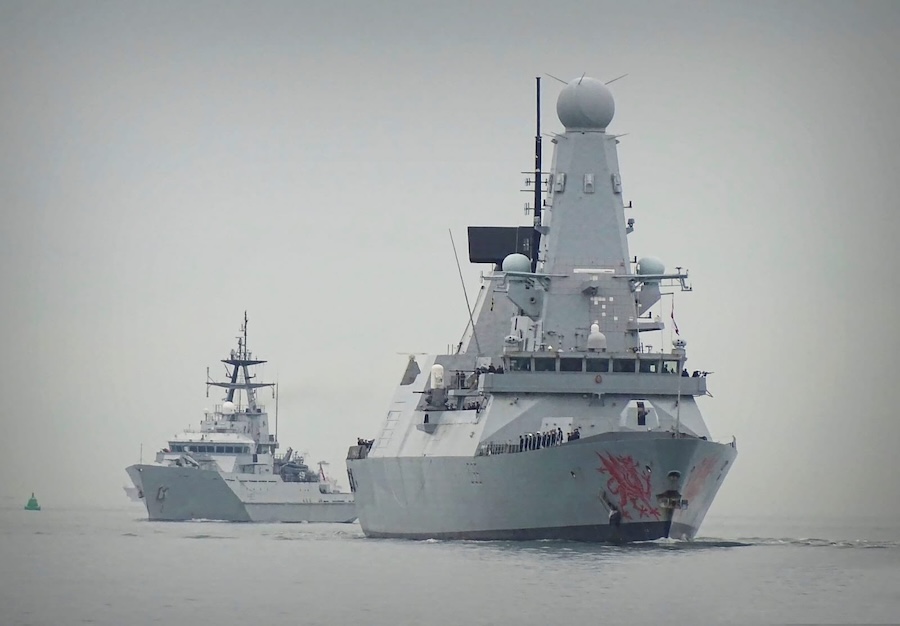
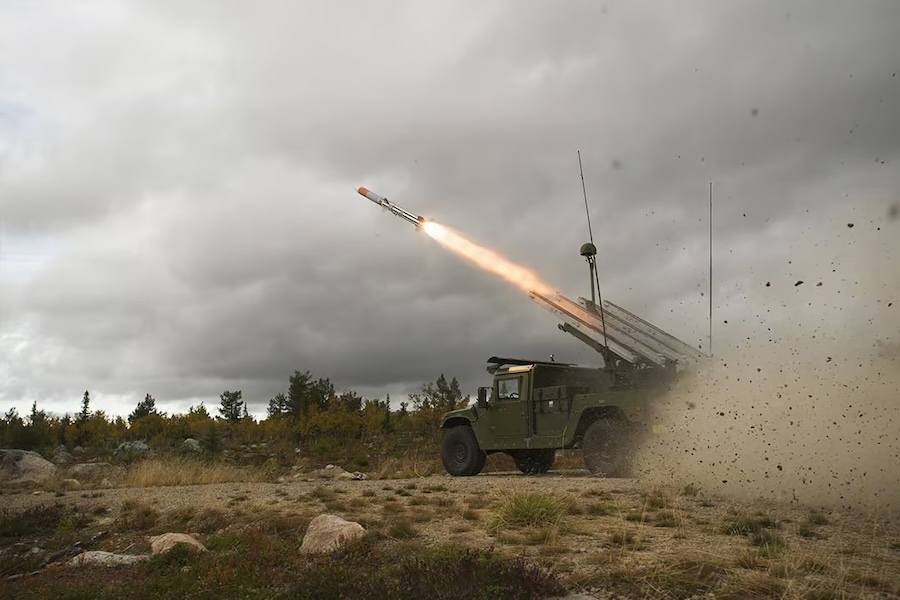
Unlike typical targets such as drones or cruise missiles, the Forbin had to engage a Hammer IR, an advanced guided bomb developed by Safran. The Hammer IR (Highly Agile Modular Munition Extended Range) converts conventional bombs into precision strike weapons using a modular guidance and propulsion system.
#Tir | 🚀 Succès pour la FDA Forbin !
La frégate de défense aérienne a intercepté une bombe A2SM (armement air-sol modulaire) tirée depuis un Rafale Marine grâce à un missile Aster 30.⚡️ Menace aérienne véloce, faible signature radar ➝ cible détruite. pic.twitter.com/DrdQUmn1xl
— Marine nationale (@MarineNationale) October 17, 2025
The Hammer IR features a nose-mounted Guidance Kit with inertial, GPS-assisted, infrared or laser guidance, and a tail-mounted Range Extension Kit with a solid-fuel rocket motor and folding fins. This system, similar to the U.S. JDAM, poses significant detection challenges due to its small radar cross-section and lack of electromagnetic emissions.
Adding to the difficulty, the Forbin was not the target of the exercise and received no target illumination from the launching aircraft, a Dassault Rafale M of the French Naval Aviation. The interception was carried out in Reflex Action Mode (RAM), meaning a reactive defence with no prior warning of the threat’s origin or timing.
The ship’s PAAMS (Principal Anti-Air Missile System) autonomously detected, classified, tracked, and destroyed the incoming munition using an MBDA Aster 30 Block 1NT missile. “All these tasks were carried out in fully automatic mode, without any human intervention,” confirmed the exercise report.
The Forbin’s sister ship, Chevalier Paul (D 621), also participated by monitoring the exercise and comparing system data during the post-event analysis. The test showcased the Horizon-class frigates’ capability to defend against next-generation aerial threats under real-time combat conditions.